|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .ebextensions | ||
| api | ||
| babybuddy | ||
| core | ||
| dashboard | ||
| etc | ||
| gulpfile.js | ||
| reports | ||
| .coveragerc | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Pipfile | ||
| Pipfile.lock | ||
| Procfile | ||
| README.md | ||
| app.json | ||
| boxfile.yml | ||
| docker-compose.yml | ||
| docker.env.example | ||
| manage.py | ||
| package-lock.json | ||
| package.json | ||
| screenshot.png | ||
| screenshot_mobile.png | ||
README.md
Baby Buddy
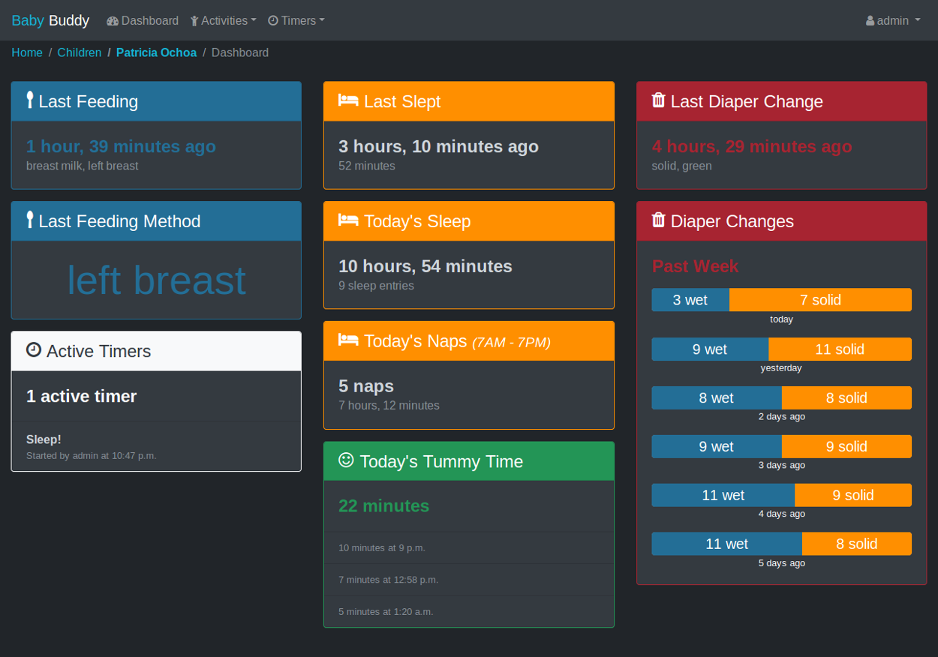
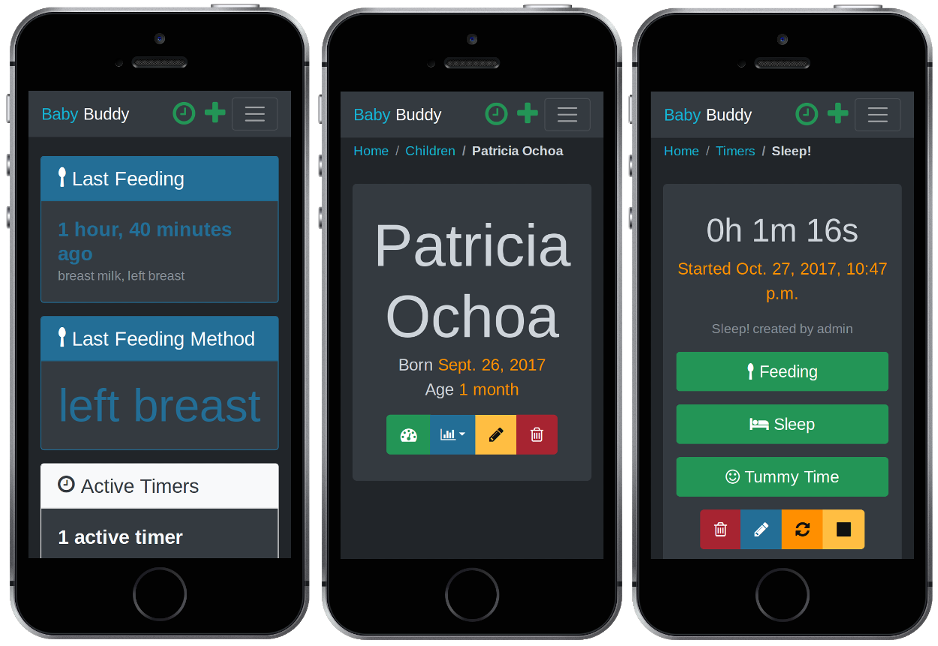
A buddy for babies! Helps caregivers track sleep, feedings, diaper changes, and tummy time to learn about and predict baby's needs without (as much) guess work.
Table of Contents
Demo
A demo of Baby Buddy is available on Heroku. The demo instance resets every hour. Login credentials are:
- Username:
admin - Password:
admin
Deployment
The default user name and password for Baby Buddy is admin/admin. For any
deployment, log in and change the default admin password immediately.
Many of Baby Buddy's configuration settings can be controlled using environment variables - see Configuration for detailed information.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
A basic Elastic Beanstalk
configuration is provided in .ebextensions/babybuddy.config. The steps
below are a rough guide to deployment. See Working with Python
for detailed information.
-
Clone/download the Baby Buddy repo
git clone https://github.com/cdubz/babybuddy.git -
Enter the cloned/downloaded directory
cd babybuddy -
Change the
SECRET_KEYvalue to something random in.ebextensions/babybuddy.config -
Create an IAM user in AWS with EB, EC2, RDS and S3 privileges.
-
Initialize the Elastic Bean application (using the IAM user from the previous step)
eb init -p python-3.6 -
Create/deploy the environment! 🚀
eb create -db -db.engine postgres
The create command will also do an initial deployment. Run eb deploy to
redeploy the app (e.g. if there are errors or settings are changed).
Docker
A Docker deploy requires Docker and Docker Compose to create two containers - one for the database and one for the application.
Baby Buddy uses a multi-stage build, which requires Docker version 17.05 or newer.
-
Copy the
docker.env.exampletodocker.envand set theALLOWED_HOSTSandSECRET_KEYvariables withincp docker.env.example docker.env editor docker.envSee Configuration for other settings that can be controlled by environment variables added to the
docker.envfile. -
Build/run the application
docker-compose up -d -
Initialize the database (first run/after updates)
docker-compose exec app python manage.py migrate -
Initialize static assets (first run/after updates)
docker-compose exec app python manage.py collectstatic
The app should now be locally available at http://127.0.0.1:8000. See Get Started, Part 6: Deploy your app for detailed information about how to deployment methods with Docker.
Nanobox
An example Nanobox configuration, boxfile.yml, is
provided with Baby Buddy. The steps below are a rough guide to deployment. See
Create and Deploy a Custom Django App
for detailed information about Nanobox's deployment and configuration process.
-
Clone/download the Baby Buddy repo
git clone https://github.com/cdubz/babybuddy.git -
Enter the cloned/downloaded directory
cd babybuddy -
Add the
SECRET_KEYandDJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULEenvironment variablesnanobox evar add DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=babybuddy.settings.nanobox nanobox evar add SECRET_KEY=<CHANGE TO SOMETHING RANDOM>See Configuration for other settings that can be controlled by environment variables.
-
Deploy! 🚀
nanobox deploy
Heroku
For manual deployments to Heroku without using the deploy button, make sure to
create two settings before pushing using heroku config:set:
heroku config:set DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=babybuddy.settings.heroku
heroku config:set SECRET_KEY=<CHANGE TO SOMETHING RANDOM>
See Configuration for other settings that can be controlled
by heroku config:set.
Manual
There are a number of ways to deploy Baby Buddy manually to any server/VPS. The application can run fine in low memory (below 1GB) situations, however a 32-bit operating system is recommended in such cases. This is primarily because the build process can be memory intensive and cause excessive memory usage on 64-bit systems. If all fails, assets can be built on a local machine and then uploaded to a server.
Requirements
- Python 2.7+, pip, pipenv
- Web server (nginx, Apache, etc.)
- Application server (uwsgi, gunicorn, etc.)
- Database (sqlite, Postgres, MySQL, etc.)
- NodeJS 8.x and NPM 5.x (for building assets)
- Gulp (for building assets)
Example deployment
This example assumes a 512MB VPS instance with Ubuntu 16.04 x32. It uses Python 3.x, nginx, uwsgi and sqlite and should be sufficient for a few users (e.g. two parents and 1+ child).
-
Install Python 3.x, pip, nginx and uwsgi
sudo apt-get install python3 python3-pip nginx uwsgi uwsgi-plugin-python3 -
Install pipenv
sudo -H pip install pipenv -
Install NodeJS, NPM and Gulp
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_8.x | sudo -E bash - sudo apt-get install nodejs sudo npm install -g gulp-cli -
Set up directories and files
sudo mkdir /var/www/babybuddy sudo chown user:user /var/www/babybuddy mkdir -p /var/www/babybuddy/data/media sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/babybuddy/data git clone https://github.com/cdubz/babybuddy.git /var/www/babybuddy/public -
Move in to the application folder
cd /var/www/babybuddy/public -
Initiate the Python environment
pipenv --three --dev -
Build static assets
npm install gulp build -
Create a production settings file and set the
SECRET_KEYandALLOWED_HOSTSvaluescp babybuddy/settings/production.example.py babybuddy/settings/production.py editor babybuddy/settings/production.py -
Initiate the application
export DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=babybuddy.settings.production gulp collectstatic gulp migrate -
Set appropriate permissions on the database and data folder
sudo chown www-data:www-data /var/www/babybuddy/data/db.sqlite3 sudo chmod 640 /var/www/babybuddy/data/db.sqlite3 sudo chmod 750 /var/www/babybuddy/data -
Create and configure the uwsgi app
sudo editor /etc/uwsgi/apps-available/babybuddy.ini sudo ln -s /etc/uwsgi/apps-available/babybuddy.ini /etc/uwsgi/apps-enabled/babybuddy.ini sudo service uwsgi restartExample config:
[uwsgi] plugins = python3 project = babybuddy base_dir = /var/www/babybuddy virtualenv = /home/user/.local/share/virtualenvs/babybuddy-XXXXXXXX chdir = %(base_dir)/babybuddy module = %(project).wsgi:application env = DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=%(project).settings.production master = True vacuum = TrueSee the uWSGI documentation for more advanced configuration details.
Note: Find the location of the pipenv virtual environment with the command
pipenv --venv. -
Create and configure the nginx server
sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/babybuddy sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/babybuddy /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/babybuddy sudo service nginx restartExample config:
upstream babybuddy { server unix:///var/run/uwsgi/app/babybuddy/socket; } server { listen 80; server_name babybuddy.example.com; location / { uwsgi_pass babybuddy; include uwsgi_params; } }See the nginx documentation for more advanced configuration details.
-
That's it (hopefully)! 🎉
Configuration
Environment variables can be used to define a number of configuration settings:
ALLOWED_HOSTS
Default: * (any)
This option may be set to a single host or comma-separated list of hosts (without spaces). This should always be set to a specific host or hosts in production deployments.
See also: Django's documentation on the ALLOWED_HOSTS setting
ALLOW_UPLOADS
Default: True
Whether or not to allow uploads (e.g. of Child photos). For some deployments (AWS, Heroku, Nanobox) this setting will default to False due to the lack of available persistent storage.
DEBUG
Default: False
When in debug mode, Baby Buddy will print much more detailed error information for exceptions. This setting should be False in production deployments.
See also Django's documentation on the DEBUG setting.
NAP_START_MAX
Default: 18:00
The maximum start time (in the instance's time zone) before which a sleep entry is consider a nap. Expects the format %H:%M.
NAP_START_MIN
Default: 06:00
The minimum start time (in the instance's time zone) after which a sleep entry is considered a nap. Expects the format %H:%M.
SECRET_KEY
Default: None
A random, unique string must be set as the "secret key" before Baby Buddy can be deployed and run.
See also Django's documentation on the SECRET_KEY setting.
TIME_ZONE
Default: Etc/UTC
The time zone to use for the instance. See List of tz database time zones for all possible values.
Development
Installation
pip install pipenv
pipenv install --dev
npm install -g gulp-cli
npm install
gulp migrate
gulp
Open http://127.0.0.1:8000 and log in with the default
user name and password (admin/admin).
Fake data
Add some fake data to the database with the following command:
gulp fake
By default, fake creates one child and 31 days of random data. Use the
--children and --days flags to change the default values, e.g.
gulp fake --children 5 --days 7 to generate five fake children and seven
days of data for each.
Testing
❗ Tests require static files to be collected, it may be necessary
to execute gulp build && gulp collectstatic before tests (if static files
have changed).
gulp test