Update category desc (#42978)
* reorganizing documents for better discoverability * adding and adjusting category descriptions for docs site --------- Co-authored-by: Jacklyn Biggin <hi@jacklyn.dev>
This commit is contained in:
parent
65d9c6764c
commit
94cacbdf56
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
category_title: Building a Woo Store
|
||||
category_slug: building-a-woo-store
|
||||
post_title: Building a Woo Store
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Discover tutorials and guides for creating custom WooCommerce stores. This section is your toolkit for building advanced, modern online shops that meet the needs of merchants and customers alike.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,16 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
post_title: WooCommerce code snippets
|
||||
category_title: Code Snippets
|
||||
category_slug: code-snippets
|
||||
post_title: Code Snippets
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Various code snippets you can add to your site to enable custom functionality:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Add a country](./add-a-country.md)
|
||||
- [Add a currency and symbol](./add-a-currency-symbol.md)
|
||||
- [Add a message above the login / register form](./before-login--register-form.md)
|
||||
- [Add or modify states](./add-or-modify-states.md)
|
||||
- [Adjust the quantity input values](./adjust-quantity-input-values.md)
|
||||
- [Change a currency symbol](./change-a-currency-symbol.md)
|
||||
- [Change number of related products output](./number-of-products-per-row.md)
|
||||
- [Rename a country](./rename-a-country.md)
|
||||
- [Unhook and remove WooCommerce emails](./unhook--remove-woocommerce-emails.md)
|
||||
- [Useful Functions](./useful-functions.md)
|
||||
Access a collection of useful code snippets to customize and enhance your WooCommerce store's functionality.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
category_title: Contributing
|
||||
category_slug: contributing
|
||||
post_title: Contributing
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Join the WooCommerce community of contributors. Find out how to build with WooCommerce and help enhance the Woo ecosystem.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
category_title: Data Management
|
||||
category_slug: data-management
|
||||
post_title: Data Management
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Master data management in WooCommerce, including documentation related to CRUD objects and data stores.
|
||||
|
|
@ -4,6 +4,4 @@ category_slug: extension-development
|
|||
post_title: Extension development
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
> ⚠️ **Notice:** This documentation is currently a **work in progress**. While it's open to the public for transparency and collaboration, please be aware that some sections might be incomplete or subject to change. We appreciate your patience and welcome any contributions!
|
||||
|
||||
This section will provide comprehensive guidance on developing extensions for WooCommerce. You will be able to dive into methodologies, best practices, and discover tutorials to create robust, user-friendly extensions that enhance the capabilities of the WooCommerce platform.
|
||||
Explore how to develop WooCommerce extensions with practical tutorials and resources ideal for initial setup and understanding the core functionalities of the platform.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,6 +4,4 @@ category_slug: getting-started
|
|||
post_title: Getting started
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
> ⚠️ **Notice:** This documentation is currently a **work in progress**. While it's open to the public for transparency and collaboration, please be aware that some sections might be incomplete or subject to change. We appreciate your patience and welcome any contributions!
|
||||
|
||||
Jumpstart your journey with WooCommerce. This category will cover the basics and essentials, from installation to initial setup, ensuring you have a solid foundation to build upon.
|
||||
Dive into WooCommerce with guides and resources ideal for initial setup and understanding the core functionalities of the platform.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,164 +1,9 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
category_title: High Performance Order Storage
|
||||
category_slug: hpos
|
||||
post_title: High Performance Order Storage (HPOS)
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
WooCommerce has traditionally stored store orders and related order information (like refunds) as custom WordPress post types or post meta records. This comes with performance issues.
|
||||
Explore High Performance Order Storage (HPOS) — a solution that provides an easy-to-understand and solid database structure – specifically designed for eCommerce needs.
|
||||
|
||||
[High-Performance Order Storage (HPOS)](https://developer.woo.com/2022/09/14/high-performance-order-storage-progress-report/) also previously known as “Custom Order Tables” is a solution that provides an easy-to-understand and solid database structure – specifically designed for eCommerce needs. It uses the WooCommerce CRUD design to store order data in custom tables – optimized for WooCommerce queries with minimal impact on the store's performance.
|
||||
|
||||
In January 2022, we published the [initial plan for the Custom Order Tables feature](https://developer.woo.com/2022/01/17/the-plan-for-the-woocommerce-custom-order-table/) and since then, we've been working hard to bring the High-Performance Order Storage (HPOS) to WooCommerce Core. In May 2022, we invited you to [test the order migration process](https://developer.woo.com/2022/05/16/call-for-early-testing-custom-order-table-migrations/) and provide feedback on how our initial work performs on real stores of varied configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
From WooCommerce 8.2, released on October 2023, [High-Performance Order Storage (HPOS)](https://developer.woo.com/2022/09/14/high-performance-order-storage-progress-report/) is officially released under the stable flag and will be enabled by default for new installations.
|
||||
|
||||
## [What's New with High-Performance Order Storage?](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-1)
|
||||
|
||||
Bringing High-Performance Order Storage (HPOS) to WooCommerce improves these three essential properties for eCommerce stores.
|
||||
|
||||
1/ **Scalability**
|
||||
|
||||
The rise in the number of customers and customer orders increases the load on your store's database – making it difficult to handle customer order requests and deliver a seamless user experience.
|
||||
|
||||
With High-Performance Order Storage, you get dedicated tables for data like orders and order addresses and thus dedicated indexes which results in fewer read/write operations and fewer busy tables. This feature enables eCommerce stores of all shapes and sizes to scale their business to their maximum potential – without expert intervention.
|
||||
|
||||
2/ **Reliability**
|
||||
|
||||
High-Performance Order Storage makes implementing and restoring targeted data backup easier. You'll no longer need to worry about losing orders, inventory numbers, or client information with reliable backup in these custom order tables. It'll also facilitate implementing read/write locks and prevent race conditions.
|
||||
|
||||
3/ **Simplicity**
|
||||
|
||||
You no longer have to go through a single huge database to locate underlying data and WooCommerce entries.
|
||||
|
||||
With High-Performance Order Storage, you can easily browse through the separate tables and easy-to-handle entries, independent of the table `_posts`, to find data or understand the table structure. It also lets you easily develop new plugins, implement designs for shops and products, and modify WooCommerce with more flexibility.
|
||||
|
||||
## [Background](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-2)
|
||||
|
||||
Before the release of version 8.2, WooCommerce relied on the `_post` and `_postmeta` table structures to store order information, which has served well over the years.
|
||||
|
||||
However, High-Performance Order Storage introduces dedicated tables for data like orders and order addresses and thus dedicated indexes which results in fewer read/write operations and fewer busy tables. This feature enables eCommerce stores of all shapes and sizes to scale their business to their maximum potential – without expert intervention.
|
||||
|
||||
The order data is synced from `_posts` and `_postmeta` table to four custom order tables:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `_wc_orders`
|
||||
2. `_wc_order_addresses`
|
||||
3. `_wc_order_operational_data`
|
||||
4. `_wc_orders_meta`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [Enabling the feature](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-3)
|
||||
|
||||
From WooCommerce 8.2, released on October 2023, HPOS is enabled by default for new installations. Existing stores can check [How to enable HPOS](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/enable-hpos.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## [Database tables](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-4)
|
||||
|
||||
A number of database tables are used to store order data by HPOS. The `get_all_table_names` method in [the OrdersTableDataStore class](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/OrdersTableDataStore.php) will return the names of all the tables.
|
||||
|
||||
## [Authoritative tables](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-5)
|
||||
|
||||
At any given time, while the HPOS feature is enabled, there are two roles for the involved database tables: _authoritative_ and _backup_. The authoritative tables are the working tables, where order data will be stored to and retrieved from during normal operation of the store. The _backup_ tables will receive a copy of the authoritative data whenever [synchronization](#synchronization) happens.
|
||||
|
||||
If the `woocommerce_custom_orders_table_enabled` options is set to true, HPOS is active and [the new tables](#database-tables) are authoritative, while the posts and post meta tables act as the backup tables. If the option is set to false, it's the other way around. The option can be changed via admin UI (WooCommerce - Settings - Advanced - Custom data stores).
|
||||
|
||||
[The CustomOrdersTableController class](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/CustomOrdersTableController.php) hooks on the `woocommerce_order_data_store` filter so that `WC_Data_Store::load( 'order' );` will return either an instance of [OrdersTableDataStore](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/OrdersTableDataStore.php) or an instance of [WC_Order_Data_Store_CPT](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/includes/data-stores/class-wc-order-data-store-cpt.php), depending on which are the authoritative tables.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to preserve data integrity, switching the authoritative tables (from the new tables to the posts table or the other way around) isn't allowed while there are orders pending synchronization.
|
||||
|
||||
## [Synchronization](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-6)
|
||||
|
||||
_Synchronization_ is the process of applying all the pending changes in the authoritative tables to the backup tables. _Orders pending synchronization_ are orders that have been modified in the authoritative tables but the changes haven't been applied to the backup tables yet.
|
||||
|
||||
This can happen in a number of ways:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Immediate synchronization
|
||||
|
||||
If the `woocommerce_custom_orders_table_data_sync_enabled` setting is set to true, synchronization happens automatically and immediately as soon as the orders are changed in the authoritative tables.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Manual synchronization
|
||||
|
||||
When immediate synchronization is disabled, it can be triggered manually via command line as follows: `wp wc cot sync`. It can also be triggered programmatically as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
$synchronizer = wc_get_container()->get(Automattic\WooCommerce\Internal\DataStores\Orders\DataSynchronizer::class);
|
||||
$order_ids = $synchronizer->get_next_batch_to_process( $batch_size );
|
||||
if ( count( $order_ids ) ) {
|
||||
$synchronizer->process_batch( $order_ids );
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where `$batch_size` is the maximum count of orders to process.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Scheduled synchronization
|
||||
|
||||
If immediate synchronization gets activated (`woocommerce_custom_orders_table_data_sync_enabled` is set to true) while there are orders pending synchronization, an instance of [DataSynchronizer](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/DataSynchronizer.php) will be enqueued using [BatchProcessingController](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/BatchProcessing/BatchProcessingController.php) so that the synchronization of created/modified/deleted orders will happen in batches via scheduled actions. This scheduling happens inside [CustomOrdersTableController](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/CustomOrdersTableController.php), by means of hooking into `woocommerce_update_options_advanced_custom_data_stores`.
|
||||
|
||||
If for some reason immediate synchronization is already active but synchronization is not scheduled, a trick to restart it is to go to the settings page (WooCommerce - Settings - Advanced - Custom data stores) and hit "Save" even without making any changes. As long as "Keep the posts table and the orders tables synchronized" is checked the synchronization scheduling will happen, even if it was checked before.
|
||||
|
||||
If the `woocommerce_auto_flip_authoritative_table_roles` option is set to true (there's a checkbox for it in the settings page), the authoritative tables will be switched automatically once all the orders have been synchronized. This is handled by [the CustomOrdersTableController class](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/CustomOrdersTableController.php).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Deletion synchronization
|
||||
|
||||
Synchronization of order deletions is tricky: if an order exists in one set of tables (new tables or posts) but not in the other, it's not clear if the missing orders need to be created or if the existing orders need to be deleted. Theoretically, the orders missing from the backup tables imply the former and the orders missing from the authoritative tables imply the latter; but that's dangerous as a bug in the involved code could easily lead to the deletion of legitimate orders.
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve a robust order deletion synchronization mechanism the following is done. Whenever an order is deleted and immediate synchronization is disabled, a record is created in the `wp_wc_orders_meta` table that has `deleted_from` as the key and the name of the authoritative table the order was deleted from (`wp_wc_orders` or the posts table). Then at synchronization time these records are processed (the corresponding orders are deleted from the corresponding tables) and deleted afterwards.
|
||||
|
||||
An exception to the above are the [placeholder records](#placeholder-records): these are deleted immediately when the corresponding order is deleted from `wp_wc_orders`, even if immediate synchronization is disabled.
|
||||
|
||||
When the “**High-Performance Order Storage**” and “**Compatibility mode**” are enabled, WooCommerce populates the HPOS tables with data from posts & postmeta tables. The synchronization between the tables is [explained in detail in this document](https://developer.woo.com/2022/09/29/high-performance-order-storage-backward-compatibility-and-synchronization/#synchronization).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> You can find a deeper explanation about the synchronization between the tables in [this document about high-performance-order-storage-backward-compatibility-and-synchronization](https://developer.woo.com/2022/09/29/high-performance-order-storage-backward-compatibility-and-synchronization/#synchronization).
|
||||
|
||||
## [Placeholder records](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-7)
|
||||
|
||||
Order IDs must match in both the authoritative tables and the backup tables, otherwise synchronization wouldn't be possible. The order IDs that are compared for order identification and synchronization purposes are the ones from the `id` field in both the `wp_wc_orders` table and the posts table.
|
||||
|
||||
If the posts table is authoritative, achieving an order ID match is easy: the record in `wp_wc_orders` is created with the same ID and that's it. However, when the new orders tables are authoritative there's a problem: the posts table is used to store multiple types of data, not only orders; and by the time synchronization needs to happen, a non-order post could already exist having the same ID as the order to synchronize.
|
||||
|
||||
To solve this, _placeholder records_ are used. Whenever the new orders tables are authoritative and immediate synchronization is disabled, creating a new order will cause a record with post type `shop_order_placehold` and the same ID as the order to be created in the posts table; this effectively "reserves" the order ID in the posts table. Then, at synchronization time, the record is filled appropriately and its post type is changed to `shop_order`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [Order Data Storage](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-8)
|
||||
|
||||
You can switch between data stores freely to sync the data between the tables.
|
||||
|
||||
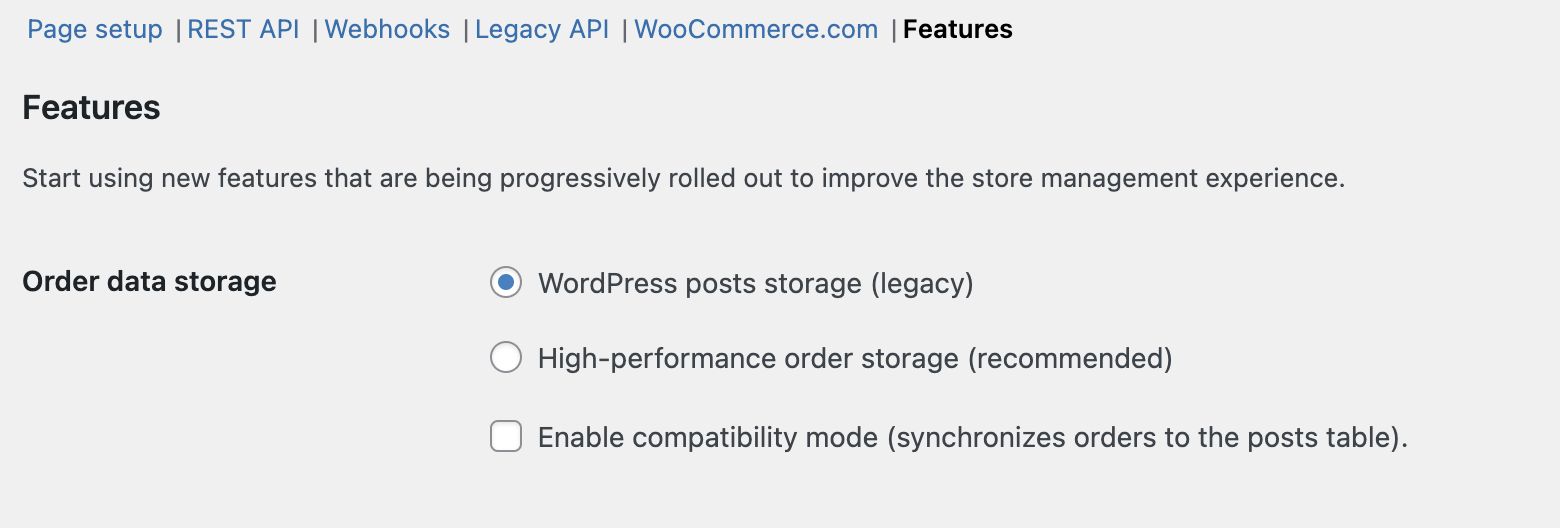
- If you select **“WordPress Post Tables”**, the system will save the order data within `_post` and `_postmeta` tables. The order tables are not utilized in this scenario.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- If you select **“High-Performance Order Storage”**, the system will save the order data within the new WooCommerce order tables
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- If you select **“WordPress Post Tables”** and **“Enable compatibility mode”**, the system will sync the order data between the posts/postmeta and the WooCommerce order tables.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [Incompatible Plugins](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-9)
|
||||
|
||||
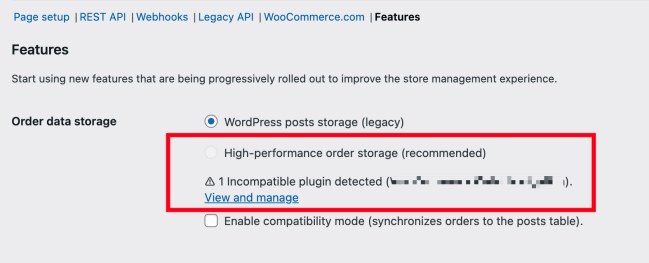
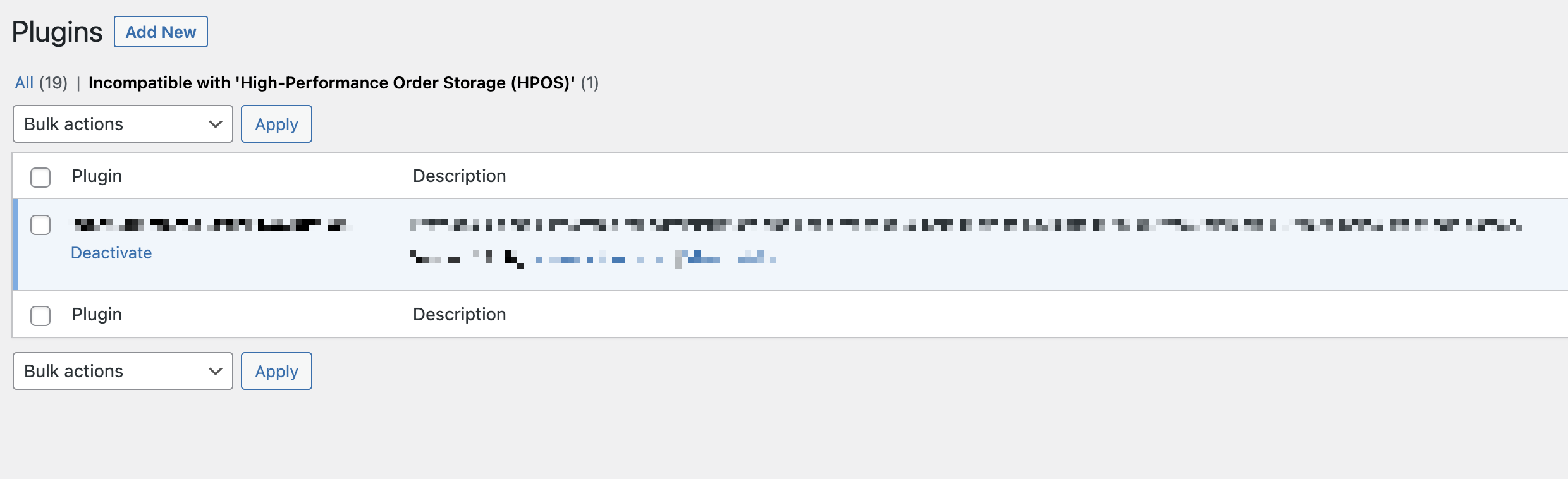
If you are using a plugin that is not compatible with High-Performance Order Storage, then the HPOS option will be disabled under **WooCommerce > Settings > Advanced > Features**.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- You can click on “**View and manage**” to review the list of incompatible plugins
|
||||
- Or you can visit `https://example.com/wp-admin/plugins.php?plugin_status=incompatible_with_feature&feature_id=custom_order_tables` to review the list of incompatible plugins (please replace `example.com` with your site domain)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> **Note:** If you are using a third-party extension that isn't working properly with High-Performance Order Storage then please notify the developers of the extension and ask them to update their extension to add support for HPOS. It's up to the extension developers to add support for HPOS. We have [developer resources and documentation](https://developer.woo.com/2022/09/14/high-performance-order-storage-progress-report/) available to help with their integration efforts.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [Disabling HPOS](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-10)
|
||||
|
||||
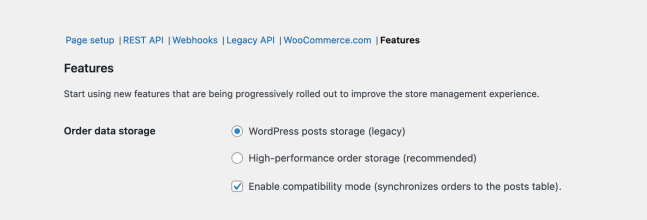
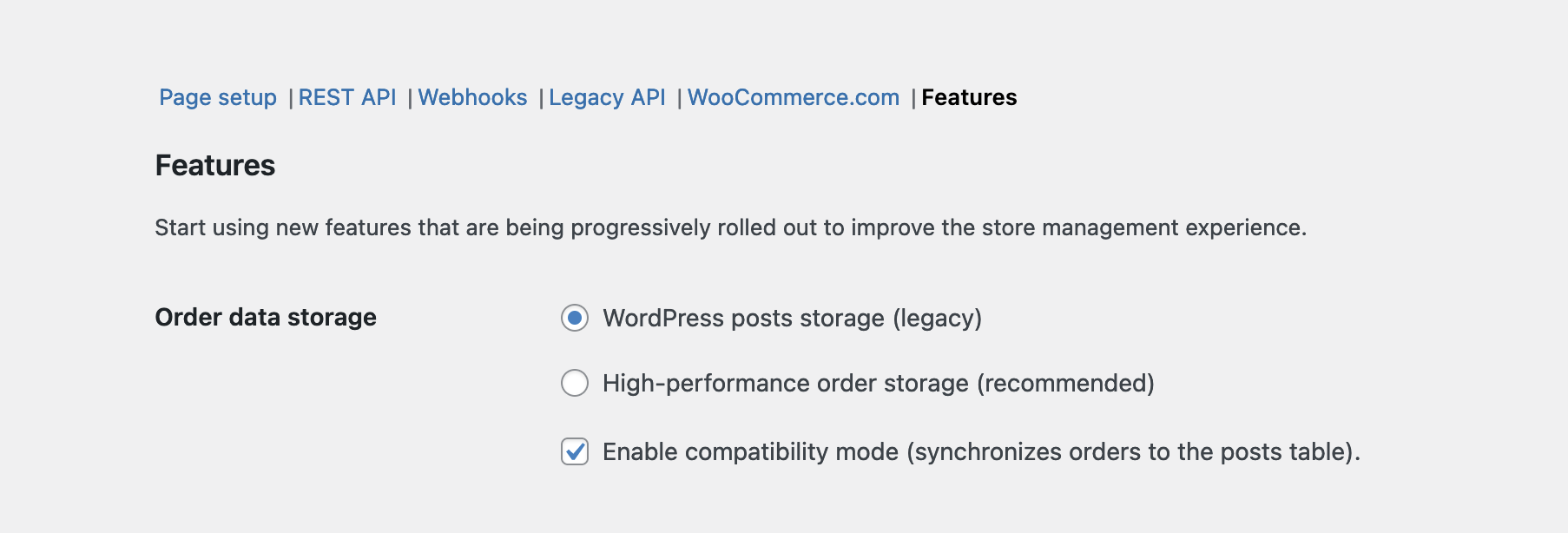
If you encounter problems or if you need to continue working with plugins that are not yet compatible with HPOS, then we recommend temporarily switching back to **WordPress posts storage**.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this, navigate to **WooCommerce ▸ Settings ▸ Advanced ▸ Features** and start by making sure that **compatibility mode** is enabled. If it was not already enabled, you may find you need to wait for some time while order data is synchronized across data-stores.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Once synchronization has completed, you can select **WordPress posts storage (legacy)** as your preferred option. You can also disable compatibility mode at this point. Once you are ready to re-enable HPOS, simply follow the instructions posted at the [start of this doc](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-3). Finally, remember to save this page between changes!
|
||||
|
||||
As noted earlier, we also strongly recommend reaching out to the support teams of any plugins that are incompatible, so they can take corrective action.
|
||||
[High-Performance Order Storage (HPOS)](https://developer.woo.com/2022/09/14/high-performance-order-storage-progress-report/) also previously known as “Custom Order Tables” is a solution that provides an easy-to-understand and solid database structure – specifically designed for eCommerce needs. It uses the WooCommerce CRUD design to store order data in custom tables – optimized for WooCommerce queries with minimal impact on the store's performance.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
post_title: High Performance Order Storage (HPOS)
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
WooCommerce has traditionally stored store orders and related order information (like refunds) as custom WordPress post types or post meta records. This comes with performance issues.
|
||||
|
||||
[High-Performance Order Storage (HPOS)](https://developer.woo.com/2022/09/14/high-performance-order-storage-progress-report/) also previously known as “Custom Order Tables” is a solution that provides an easy-to-understand and solid database structure – specifically designed for eCommerce needs. It uses the WooCommerce CRUD design to store order data in custom tables – optimized for WooCommerce queries with minimal impact on the store’s performance.
|
||||
|
||||
In January 2022, we published the [initial plan for the Custom Order Tables feature](https://developer.woo.com/2022/01/17/the-plan-for-the-woocommerce-custom-order-table/) and since then, we’ve been working hard to bring the High-Performance Order Storage (HPOS) to WooCommerce Core. In May 2022, we invited you to [test the order migration process](https://developer.woo.com/2022/05/16/call-for-early-testing-custom-order-table-migrations/) and provide feedback on how our initial work performs on real stores of varied configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
From WooCommerce 8.2, released on October 2023, [High-Performance Order Storage (HPOS)](https://developer.woo.com/2022/09/14/high-performance-order-storage-progress-report/) is officially released under the stable flag and will be enabled by default for new installations.
|
||||
|
||||
## [What’s New with High-Performance Order Storage?](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-1)
|
||||
|
||||
Bringing High-Performance Order Storage (HPOS) to WooCommerce improves these three essential properties for eCommerce stores.
|
||||
|
||||
1/ **Scalability**
|
||||
|
||||
The rise in the number of customers and customer orders increases the load on your store’s database – making it difficult to handle customer order requests and deliver a seamless user experience.
|
||||
|
||||
With High-Performance Order Storage, you get dedicated tables for data like orders and order addresses and thus dedicated indexes which results in fewer read/write operations and fewer busy tables. This feature enables eCommerce stores of all shapes and sizes to scale their business to their maximum potential – without expert intervention.
|
||||
|
||||
2/ **Reliability**
|
||||
|
||||
High-Performance Order Storage makes implementing and restoring targeted data backup easier. You’ll no longer need to worry about losing orders, inventory numbers, or client information with reliable backup in these custom order tables. It’ll also facilitate implementing read/write locks and prevent race conditions.
|
||||
|
||||
3/ **Simplicity**
|
||||
|
||||
You no longer have to go through a single huge database to locate underlying data and WooCommerce entries.
|
||||
|
||||
With High-Performance Order Storage, you can easily browse through the separate tables and easy-to-handle entries, independent of the table `_posts`, to find data or understand the table structure. It also lets you easily develop new plugins, implement designs for shops and products, and modify WooCommerce with more flexibility.
|
||||
|
||||
## [Background](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-2)
|
||||
|
||||
Before the release of version 8.2, WooCommerce relied on the `_post` and `_postmeta` table structures to store order information, which has served well over the years.
|
||||
|
||||
However, High-Performance Order Storage introduces dedicated tables for data like orders and order addresses and thus dedicated indexes which results in fewer read/write operations and fewer busy tables. This feature enables eCommerce stores of all shapes and sizes to scale their business to their maximum potential – without expert intervention.
|
||||
|
||||
The order data is synced from `_posts` and `_postmeta` table to four custom order tables:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `_wc_orders`
|
||||
2. `_wc_order_addresses`
|
||||
3. `_wc_order_operational_data`
|
||||
4. `_wc_orders_meta`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [Enabling the feature](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-3)
|
||||
|
||||
From WooCommerce 8.2, released on October 2023, HPOS is enabled by default for new installations. Existing stores can check [How to enable HPOS](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/enable-hpos.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## [Database tables](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-4)
|
||||
|
||||
A number of database tables are used to store order data by HPOS. The `get_all_table_names` method in [the OrdersTableDataStore class](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/OrdersTableDataStore.php) will return the names of all the tables.
|
||||
|
||||
## [Authoritative tables](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-5)
|
||||
|
||||
At any given time, while the HPOS feature is enabled, there are two roles for the involved database tables: _authoritative_ and _backup_. The authoritative tables are the working tables, where order data will be stored to and retrieved from during normal operation of the store. The _backup_ tables will receive a copy of the authoritative data whenever [synchronization](#synchronization) happens.
|
||||
|
||||
If the `woocommerce_custom_orders_table_enabled` options is set to true, HPOS is active and [the new tables](#database-tables) are authoritative, while the posts and post meta tables act as the backup tables. If the option is set to false, it's the other way around. The option can be changed via admin UI (WooCommerce - Settings - Advanced - Custom data stores).
|
||||
|
||||
[The CustomOrdersTableController class](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/CustomOrdersTableController.php) hooks on the `woocommerce_order_data_store` filter so that `WC_Data_Store::load( 'order' );` will return either an instance of [OrdersTableDataStore](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/OrdersTableDataStore.php) or an instance of [WC_Order_Data_Store_CPT](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/includes/data-stores/class-wc-order-data-store-cpt.php), depending on which are the authoritative tables.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to preserve data integrity, switching the authoritative tables (from the new tables to the posts table or the other way around) isn't allowed while there are orders pending synchronization.
|
||||
|
||||
## [Synchronization](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-6)
|
||||
|
||||
_Synchronization_ is the process of applying all the pending changes in the authoritative tables to the backup tables. _Orders pending synchronization_ are orders that have been modified in the authoritative tables but the changes haven't been applied to the backup tables yet.
|
||||
|
||||
This can happen in a number of ways:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Immediate synchronization
|
||||
|
||||
If the `woocommerce_custom_orders_table_data_sync_enabled` setting is set to true, synchronization happens automatically and immediately as soon as the orders are changed in the authoritative tables.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Manual synchronization
|
||||
|
||||
When immediate synchronization is disabled, it can be triggered manually via command line as follows: `wp wc cot sync`. It can also be triggered programmatically as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
$synchronizer = wc_get_container()->get(Automattic\WooCommerce\Internal\DataStores\Orders\DataSynchronizer::class);
|
||||
$order_ids = $synchronizer->get_next_batch_to_process( $batch_size );
|
||||
if ( count( $order_ids ) ) {
|
||||
$synchronizer->process_batch( $order_ids );
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where `$batch_size` is the maximum count of orders to process.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Scheduled synchronization
|
||||
|
||||
If immediate synchronization gets activated (`woocommerce_custom_orders_table_data_sync_enabled` is set to true) while there are orders pending synchronization, an instance of [DataSynchronizer](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/DataSynchronizer.php) will be enqueued using [BatchProcessingController](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/BatchProcessing/BatchProcessingController.php) so that the synchronization of created/modified/deleted orders will happen in batches via scheduled actions. This scheduling happens inside [CustomOrdersTableController](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/CustomOrdersTableController.php), by means of hooking into `woocommerce_update_options_advanced_custom_data_stores`.
|
||||
|
||||
If for some reason immediate synchronization is already active but synchronization is not scheduled, a trick to restart it is to go to the settings page (WooCommerce - Settings - Advanced - Custom data stores) and hit "Save" even without making any changes. As long as "Keep the posts table and the orders tables synchronized" is checked the synchronization scheduling will happen, even if it was checked before.
|
||||
|
||||
If the `woocommerce_auto_flip_authoritative_table_roles` option is set to true (there's a checkbox for it in the settings page), the authoritative tables will be switched automatically once all the orders have been synchronized. This is handled by [the CustomOrdersTableController class](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Internal/DataStores/Orders/CustomOrdersTableController.php).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Deletion synchronization
|
||||
|
||||
Synchronization of order deletions is tricky: if an order exists in one set of tables (new tables or posts) but not in the other, it's not clear if the missing orders need to be created or if the existing orders need to be deleted. Theoretically, the orders missing from the backup tables imply the former and the orders missing from the authoritative tables imply the latter; but that's dangerous as a bug in the involved code could easily lead to the deletion of legitimate orders.
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve a robust order deletion synchronization mechanism the following is done. Whenever an order is deleted and immediate synchronization is disabled, a record is created in the `wp_wc_orders_meta` table that has `deleted_from` as the key and the name of the authoritative table the order was deleted from (`wp_wc_orders` or the posts table). Then at synchronization time these records are processed (the corresponding orders are deleted from the corresponding tables) and deleted afterwards.
|
||||
|
||||
An exception to the above are the [placeholder records](#placeholder-records): these are deleted immediately when the corresponding order is deleted from `wp_wc_orders`, even if immediate synchronization is disabled.
|
||||
|
||||
When the “**High-Performance Order Storage**” and “**Compatibility mode**” are enabled, WooCommerce populates the HPOS tables with data from posts & postmeta tables. The synchronization between the tables is [explained in detail in this document](https://developer.woo.com/2022/09/29/high-performance-order-storage-backward-compatibility-and-synchronization/#synchronization).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> You can find a deeper explanation about the synchronization between the tables in [this document about high-performance-order-storage-backward-compatibility-and-synchronization](https://developer.woo.com/2022/09/29/high-performance-order-storage-backward-compatibility-and-synchronization/#synchronization).
|
||||
|
||||
## [Placeholder records](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-7)
|
||||
|
||||
Order IDs must match in both the authoritative tables and the backup tables, otherwise synchronization wouldn't be possible. The order IDs that are compared for order identification and synchronization purposes are the ones from the `id` field in both the `wp_wc_orders` table and the posts table.
|
||||
|
||||
If the posts table is authoritative, achieving an order ID match is easy: the record in `wp_wc_orders` is created with the same ID and that's it. However, when the new orders tables are authoritative there's a problem: the posts table is used to store multiple types of data, not only orders; and by the time synchronization needs to happen, a non-order post could already exist having the same ID as the order to synchronize.
|
||||
|
||||
To solve this, _placeholder records_ are used. Whenever the new orders tables are authoritative and immediate synchronization is disabled, creating a new order will cause a record with post type `shop_order_placehold` and the same ID as the order to be created in the posts table; this effectively "reserves" the order ID in the posts table. Then, at synchronization time, the record is filled appropriately and its post type is changed to `shop_order`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [Order Data Storage](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-8)
|
||||
|
||||
You can switch between data stores freely to sync the data between the tables.
|
||||
|
||||
- If you select **“WordPress Post Tables”**, the system will save the order data within `_post` and `_postmeta` tables. The order tables are not utilized in this scenario.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- If you select **“High-Performance Order Storage”**, the system will save the order data within the new WooCommerce order tables
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- If you select **“WordPress Post Tables”** and **“Enable compatibility mode”**, the system will sync the order data between the posts/postmeta and the WooCommerce order tables.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [Incompatible Plugins](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-9)
|
||||
|
||||
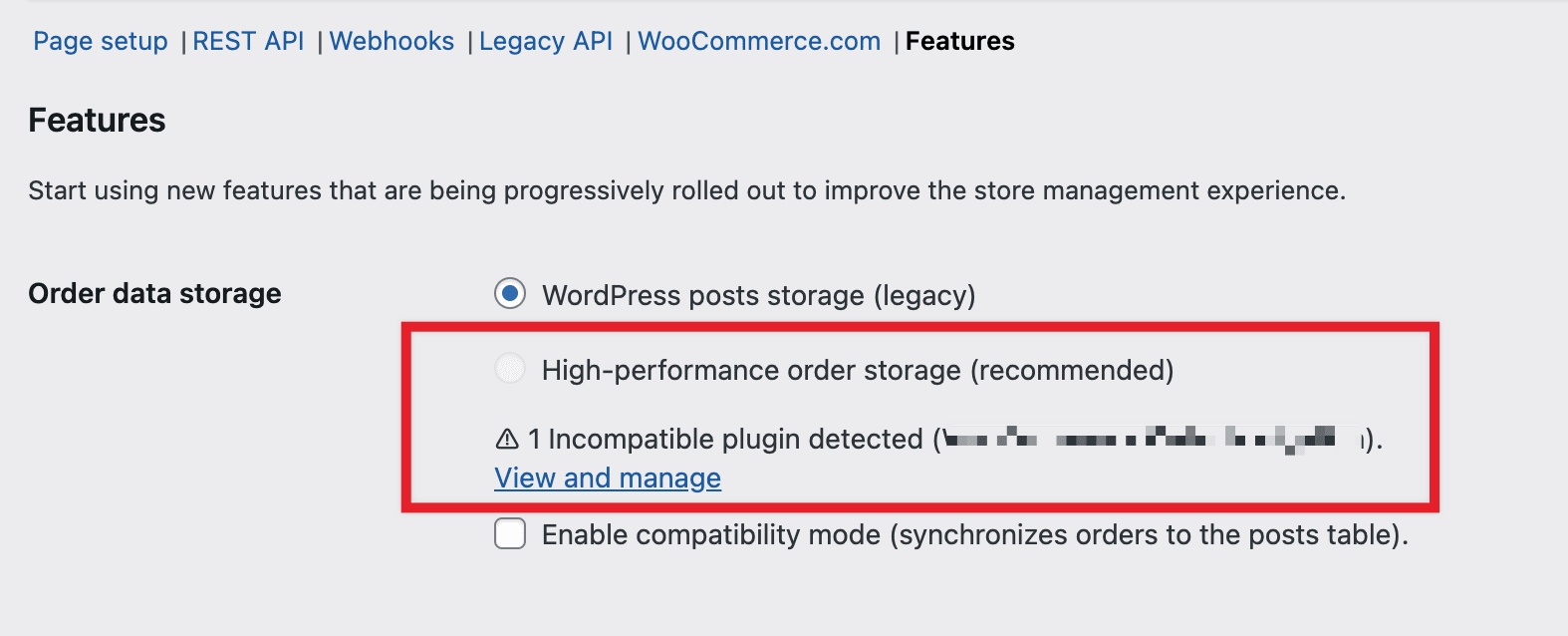
If you are using a plugin that is not compatible with High-Performance Order Storage, then the HPOS option will be disabled under **WooCommerce > Settings > Advanced > Features**.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- You can click on “**View and manage**” to review the list of incompatible plugins
|
||||
- Or you can visit `https://example.com/wp-admin/plugins.php?plugin_status=incompatible_with_feature&feature_id=custom_order_tables` to review the list of incompatible plugins (please replace `example.com` with your site domain)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> **Note:** If you are using a third-party extension that isn’t working properly with High-Performance Order Storage then please notify the developers of the extension and ask them to update their extension to add support for HPOS. It’s up to the extension developers to add support for HPOS. We have [developer resources and documentation](https://developer.woo.com/2022/09/14/high-performance-order-storage-progress-report/) available to help with their integration efforts.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [Disabling HPOS](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-10)
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter problems or if you need to continue working with plugins that are not yet compatible with HPOS, then we recommend temporarily switching back to **WordPress posts storage**.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this, navigate to **WooCommerce ▸ Settings ▸ Advanced ▸ Features** and start by making sure that **compatibility mode** is enabled. If it was not already enabled, you may find you need to wait for some time while order data is synchronized across data-stores.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Once synchronization has completed, you can select **WordPress posts storage (legacy)** as your preferred option. You can also disable compatibility mode at this point. Once you are ready to re-enable HPOS, simply follow the instructions posted at the [start of this doc](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/docs/high-performance-order-storage/#section-3). Finally, remember to save this page between changes!
|
||||
|
||||
As noted earlier, we also strongly recommend reaching out to the support teams of any plugins that are incompatible, so they can take corrective action.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
category_title: Localizatiion and Translation
|
||||
category_slug: localization-translation
|
||||
post_title: Localizatiion and Translation
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Tailor your WooCommerce store for global audiences with guides on setting up and translating Woo in your language.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
category_title: Payments
|
||||
category_slug: payments
|
||||
post_title: Payments
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Get insights into integrating and customizing various payment gateways in WooCommerce for secure and efficient transactions.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,42 +1,9 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
post_title: Product Editor Development Handbook
|
||||
category_title: Product Editor
|
||||
category_slug: product-editor
|
||||
post_title: Product Editor
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
> ⚠️ **Notice:** This documentation is currently a **work in progress**. Please be aware that some sections might be incomplete or subject to change. We appreciate your patience and welcome any contributions!
|
||||
Discover how to customize the WooCommerce product editor, from extending product data to adding unique functionalities.
|
||||
|
||||
This handbook is a guide for extension developers looking to add support for the new product editor in their extensions. The product editor uses [Gutenberg's Block Editor](https://github.com/WordPress/gutenberg/tree/trunk/packages/block-editor), which is going to help WooCommerce evolve alongside the WordPress ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
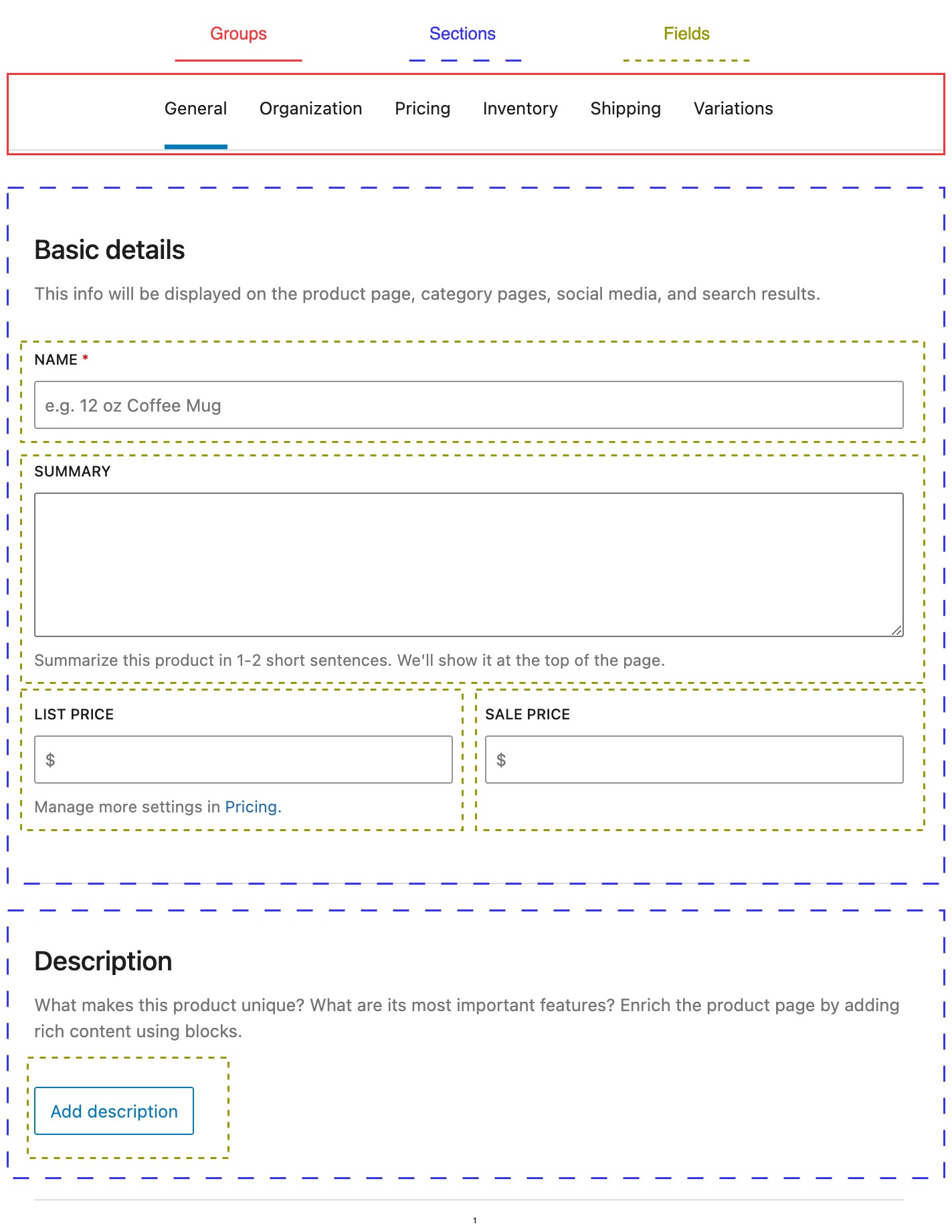
The product editor's UI consists of Groups (currently rendered as tabs), Sections, and Fields, which are all blocks. For guidelines on how to extend the product editor (e.g. where to add blocks), please refer to the [Product Editor Extensibility Guidelines](./product-editor-extensibility-guidelines.md).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The form's structure is defined in PHP using a Template, which is a tree structure of blocks. The template can be modified by using the Template API to add new Groups, Sections, and Fields as well as remove existing ones.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about when to perform template modifications, see the [block template lifecycle](./block-template-lifecycle.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Many extensibility implementations can be done using only the PHP-based Block Template API alongside our library of [generic blocks](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/packages/js/product-editor/src/blocks/generic/README.md). More complex interactivity can be implemented using JavaScript and React (the same library used to implement the core blocks used in the product editor). [@woocommerce/create-product-editor-block](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/packages/js/create-product-editor-block/README.md) can help scaffold a development environment with JavaScript and React.
|
||||
|
||||
## Declaring compatibility with the product editor
|
||||
|
||||
To declare compatibility with the product editor, add the following to your plugin's root PHP file:
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
use Automattic\WooCommerce\Utilities\FeaturesUtil;
|
||||
|
||||
add_action(
|
||||
'before_woocommerce_init',
|
||||
function() {
|
||||
if ( class_exists( FeaturesUtil::class ) ) {
|
||||
FeaturesUtil::declare_compatibility( 'product_block_editor', plugin_basename( __FILE__ ), true );
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that this check is currently not being enforced: the product editor can still be enabled even without this declaration. However, we might enforce this in the future, so it is recommended to declare compatibility as soon as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
## Related documentation
|
||||
|
||||
- [Examples on Template API usage](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Admin/Features/ProductBlockEditor/ProductTemplates/README.md)
|
||||
- [Related hooks and Template API documentation](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/plugins/woocommerce/src/Admin/BlockTemplates/README.md)
|
||||
- [Generic blocks documentation](https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/blob/trunk/packages/js/product-editor/src/blocks/generic/README.md)
|
||||
This handbook is a guide for extension developers looking to add support for the new product editor in their extensions. The product editor uses [Gutenberg's Block Editor](https://github.com/WordPress/gutenberg/tree/trunk/packages/block-editor), which is going to help WooCommerce evolve alongside the WordPress ecosystem.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
post_title: Product Editor Development Handbook
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
This handbook is a guide for extension developers looking to add support for the new product editor in their extensions. The product editor uses [Gutenberg's Block Editor](https://github.com/WordPress/gutenberg/tree/trunk/packages/block-editor), which is going to help WooCommerce evolve alongside the WordPress ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
The product editor's UI consists of Groups (currently rendered as tabs), Sections, and Fields, which are all blocks. For guidelines on how to extend the product editor (e.g. where to add blocks), please refer to the [Product Editor Extensibility Guidelines](./product-editor-extensibility-guidelines.md).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The form's structure is defined in PHP using a Template, which is a tree structure of blocks. The template can be modified by using the Template API to add new Groups, Sections, and Fields as well as remove existing ones.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about when to perform template modifications, see the [block template lifecycle](./block-template-lifecycle.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Many extensibility implementations can be done using only the PHP-based Block Template API alongside our library of [generic blocks](../../packages/js/product-editor/src/blocks/generic/README.md). More complex interactivity can be implemented using JavaScript and React (the same library used to implement the core blocks used in the product editor). [@woocommerce/create-product-editor-block](../../packages/js/create-product-editor-block/README.md) can help scaffold a development environment with JavaScript and React.
|
||||
|
||||
## Declaring compatibility with the product editor
|
||||
|
||||
To declare compatibility with the product editor, add the following to your plugin's root PHP file:
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
use Automattic\WooCommerce\Utilities\FeaturesUtil;
|
||||
|
||||
add_action(
|
||||
'before_woocommerce_init',
|
||||
function() {
|
||||
if ( class_exists( FeaturesUtil::class ) ) {
|
||||
FeaturesUtil::declare_compatibility( 'product_block_editor', plugin_basename( __FILE__ ), true );
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that this check is currently not being enforced: the product editor can still be enabled even without this declaration. However, we might enforce this in the future, so it is recommended to declare compatibility as soon as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
## Related documentation
|
||||
|
||||
- [Examples on Template API usage](../../plugins/woocommerce/src/Admin/Features/ProductBlockEditor/ProductTemplates/README.md)
|
||||
- [Related hooks and Template API documentation](../../plugins/woocommerce/src/Admin/BlockTemplates/README.md)
|
||||
- [Generic blocks documentation](../../packages/js/product-editor/src/blocks/generic/README.md)
|
||||
|
|
@ -4,6 +4,4 @@ category_slug: quality-and-best-practices
|
|||
post_title: Quality and best practices
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
> ⚠️ **Notice:** This documentation is currently a **work in progress**. While it's open to the public for transparency and collaboration, please be aware that some sections might be incomplete or subject to change. We appreciate your patience and welcome any contributions!
|
||||
|
||||
Ensuring the quality of your WooCommerce projects is essential. This section will delve into quality exoectations, best practices, coding standards, and other methodologies to ensure your projects stand out in terms of reliability, efficiency, user experience, and more.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,6 +4,4 @@ category_slug: reporting
|
|||
post_title: Reporting
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
> ⚠️ **Notice:** This documentation is currently a **work in progress**. While it's open to the public for transparency and collaboration, please be aware that some sections might be incomplete or subject to change. We appreciate your patience and welcome any contributions!
|
||||
|
||||
Understanding your WooCommerce store's performance is crucial. This section will provide insights into generating, understanding, and optimizing reports to make informed decisions about WooCommerce projects.
|
||||
Understand Woo's reporting capabilities. Learn to generate, understand, and optimize reports to make informed decisions about your WooCommerce projects.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,6 +4,4 @@ category_slug: rest-api
|
|||
post_title: REST API
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
> ⚠️ **Notice:** This documentation is currently a **work in progress**. While it's open to the public for transparency and collaboration, please be aware that some sections might be incomplete or subject to change. We appreciate your patience and welcome any contributions!
|
||||
|
||||
Harness the power of WooCommerce's REST API. This section will help you discover comprehensive documentation on endpoints, authentication, and best practices, aiding developers in integrating and manipulating WooCommerce functionalities programmatically.
|
||||
Utilize the WooCommerce REST API for advanced integrations, data manipulation, and building headless ecommerce solutions.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,6 +4,4 @@ category_slug: security
|
|||
post_title: Security
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
> ⚠️ **Notice:** This documentation is currently a **work in progress**. While it's open to the public for transparency and collaboration, please be aware that some sections might be incomplete or subject to change. We appreciate your patience and welcome any contributions!
|
||||
|
||||
Security is paramount. This section will dive into best practices, guidelines, and insights to ensure your WooCommerce projects remain secure from threats.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
category_title: Shipping
|
||||
category_slug: shipping
|
||||
post_title: Shipping
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Delve into extending shipping functionality through adding custom shipping methods, integrating advanced carrier APIs, and developing tailored shipping solutions to elevate the ecommerce experience.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
post_title: Theme Design and Development at Woo
|
||||
category_title: Theme Development
|
||||
category_slug: theme-development
|
||||
post_title: Theme Development
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Classic Themes
|
||||
|
||||
## Block Themes
|
||||
|
||||
* [Marketplace Guidelines](marketplace-guidelines.md)
|
||||
Learn to design and integrate custom themes in WooCommerce, focusing on responsive design and ecommerce optimization.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
category_title: Tutorials
|
||||
category_slug: tutorials
|
||||
post_title: Tutorials
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
> ⚠️ **Notice:** This documentation is currently a **work in progress**. While it's open to the public for transparency and collaboration, please be aware that some sections might be incomplete or subject to change. We appreciate your patience and welcome any contributions!
|
||||
|
||||
This section will contain step-by-step guides and walkthroughs tailored for both novice and seasoned WooCommerce enthusiasts. Whether it's setting up a new feature or diving into complex customizations, our tutorials will cover a wide range of topics to help you achieve your goals.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
category_title: User Experience
|
||||
category_slug: user-experience
|
||||
post_title: User Experience
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Create engaging user experiences in WooCommerce stores, focusing on UX design, checkout customization, and user interaction.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
category_title: WC CLI
|
||||
category_slug: wc-cli
|
||||
post_title: WC CLI
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Master the WooCommerce Command Line Interface for efficient store management and automation with detailed command line tutorials.
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue